Electricity in any environment can be dangerous but bathrooms are especially dangerous due to the presence of water (hence the need for electrical safe zones in a bathroom). As such only competent persons (ie, trained and qualified electricians) should work with electricity in bathrooms.
Look here if you need to find a reliable electrician near you.
That said, even as a DIY enthusiast it is important to understand the safety zones in bathrooms (electrical safety zones in a bathroom) so that you will know what types of electrical devices can and cannot be used when you are planning and laying out your bathroom.
Also from a safety perspective you can immediately see if there are any items currently in your bathroom that shouldn’t be there or are currently in teh wrong zone.
Electrical Zones in Bathrooms in the UK
The regulations (BS 7671:2008 Requirements for Electrical Installations, section 701, published in 2008) divide the bathroom into zones depending on their electrical risk. Each zone has different limitations about the types of electrical devices that can be used in them.
Here is an illustration of the zones as you would typically find them in your bathroom:
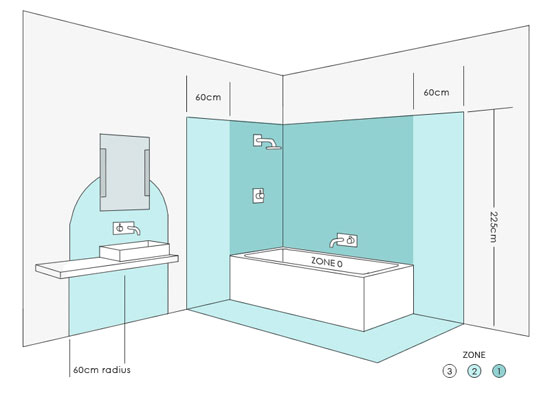
UK Electrical Zones in Bathrooms
Here are the zones explained in more detail:
Bathroom Zone 0
This is the area that is inside the bath or shower tray. If there is no shower tray present then this (and zone 1) extend to 1.2m from the ‘fixed water outlet’ or shower head.
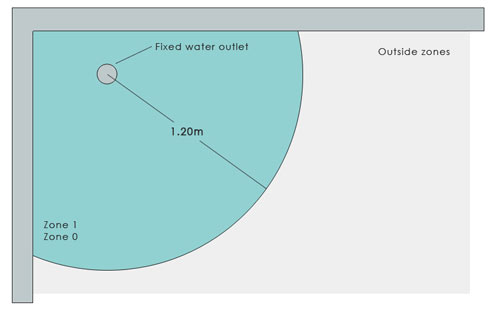
Electrical Safety Zones 0 and 1 for showers without shower basins or trays
Bathroom Zone 1
This is the area directly above zone 0 (which is the outer edge of the shower basin or bath) extending to the horizontal ceiling or 225cm from the floor, whichever is lower. If the shower head is higher than this then the zone extends to a line horizontal with it.
Zone 1 also extends to a circumference of 1.2m from the shower head if there is no shower tray or basin and it rises to the heights described above (see above diagram).
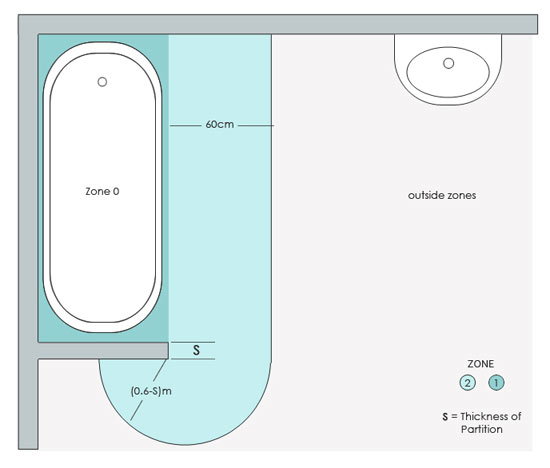
Under the bath is also considered to be Zone 1 if it is accessible without the use of tools such as a screwdriver. If you do need to access this space with the use of a tool, then it is considered an “Outside Zone&rdquo.
The Electrical Bathroom Zones around a Bath
Bathroom Zone 2
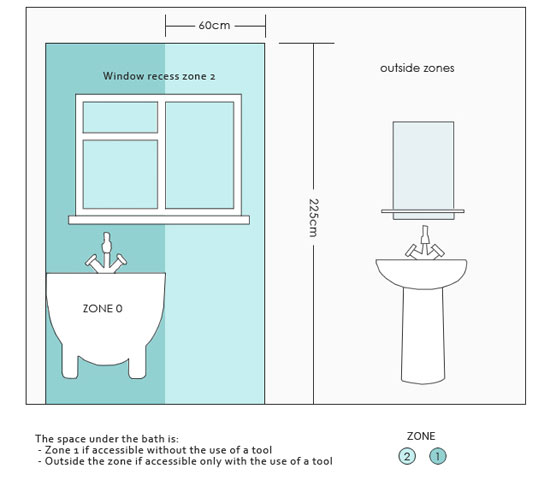
This zone extends beyond zone 1 by 60 cm and extends to the same height. This includes 60 cm beyond a partition wall marking the end of zone 1.
The Extent of Zone 2 when using UK bathroom electrical safety zones
Window recesses that extend into the area zone 1 occupies are also considered as zone 2.
Outside Zones (aka Zone 3)
These are the areas beyond zones 0, 1 and 2. This was previously known as Zone 3 and is essentially anything in the bathroom that is not zones 0-2.
This also includes the area under the bath if it requires a tool to remove the bath panel to access this area.
Electrical Devices That you are Allowed in Bathrooms and Where
Now that we understand where the electrical zones are in a bathroom we can now see what restrictions there are on devices that are allowed to exist in those zones.
The following table describes the types of devices that are allowed in each zone:
| Zone | IP Rating | Class | Comments |
| Zone 0 | IPX7 | low voltage (max. 12 volts) | |
| Zone 1 | IPX4 (IPX5*) | SELV (transformer located beyond zone 2) | SELV = Separated Extra Low Voltage |
| Zone 2 | IPX4 (IPX5*) | SELV (transformer located beyond zone 2) | Shaver sockets are an exception, not being IPX4, then can be fitted where direct spray is unlikely |
| Outside Zones | (IPX5*) | Portable equipment is allowed, however the flex should allow their use inside the zones ** |
* Outside the zones there is no IP stipulated in the regulations and when a device exists inside a given zone, if it is likely to be exposed to water jets it should conform to at least IPX5 specifications, which being a bathroom it probably will for example when being cleaned.
** Sockets are allowed in bathrooms, but they must be at least 3m horizontally from the boundary of zone 1.
Ratings of Electrical Devices for Bathrooms
A system of identifying the level of protection for moisture and dust, called “Ingress Protection” Ratings or IP Rating for short is used to determine the levels of protection needed for particular zones. The rating is written in a standard format:

What the IP77 rating means
- The letters stand for Ingress Protection
- The first number is the protection level from intrusion; effectively dust getting into the device, in a scale of 1 (no protection) to 7 (totally dust tight)
- The second number is the level of protection against moisture from 1 (no protection) to 9 (prolonged immersion under pressure)
- An “X” can be used to replace the numbers if the device is not rated for that specification
Electrical devices that are designed for use in a bathroom will have an IP rating. These include extractor fans, heaters, pumps and lighting. Shaver Sockets are not IP rated, but they are a special case as described above.
Devices that can be used in bathrooms need to be low Voltage and in terms of this there are two classes:
- SELV – Separated Extra Low Voltage: These are devices where the output is isolated from the input i.e. there is no possibility of a high voltage getting to the lower voltage appliance via the transformer
- PELV – Protective Extra Low Voltage: These are devices which are connected to earth via the transformer. A PELV is a SELF with an independent earth wire. If there is any kind of short circuit this cannot effect the user via a shared earth
Circuit Protection is Bathrooms
All circuits (lighting, electric showers, heated rails, etc) in bathrooms must be protected by an RCD, or Residual Current Device, that cannot exceed 30mA.
Some Electrical Appliances Commonly Fitted in Bathrooms
Here follows some specific information about electrical devices that are typically installed in bathrooms. It is important to ensure, even if the device meets all the requirements of the regulations, that it has been approved for installation in a bathroom by the manufacturer.
Extractor Fans: These can be installed in zones 1 or 2 if they have the correct IP rating for moisture. If the extractor fan is on the lighting circuit, which it commonly is in a bathroom it should have its own seperate isolation switch which should be fitted outside the bathroom.
Lights Above Showers (or baths)
When it comes to bathroom lighting zones lights can be fitted above showers in zone 1 if required if they have the correct IP rating.
Sockets and Light Switches
Sockets and light switches can be fitted in bathrooms under certain circumstances. As we mentioned above sockets have to be a minimum of 3m horizontally away from the nearest boundary for zone 1.
Pull cord switches are allowed in Zones 1 and 2 and are recommended as they are suitable for environments with high humidity and condensation levels. Plate switches can be used outside the zones and when deemed suitable for use in a bathroom by the manufacture.
Shaver sockets are a special case as we have mentioned above. Despite not being IPX4 rated they can be fitted in Zone 2 where direct spray or water contact is unlikely. See For more information see our how to fit a shave socket project here.
Washing Machines and Tumble Dryers
These can be installed in a bathroom if required, provided they are supplied with power from a fused socket (see above), they are protected by a 30mA RCD and the manufacture permits their installation in this way.
The zones in a bathroom are an important safety feature and designed to keep us safe, both when installing devices and when using them. Remember that to work with electricity in a bathroom you should be a competent and qualified Part P registered electrician.

